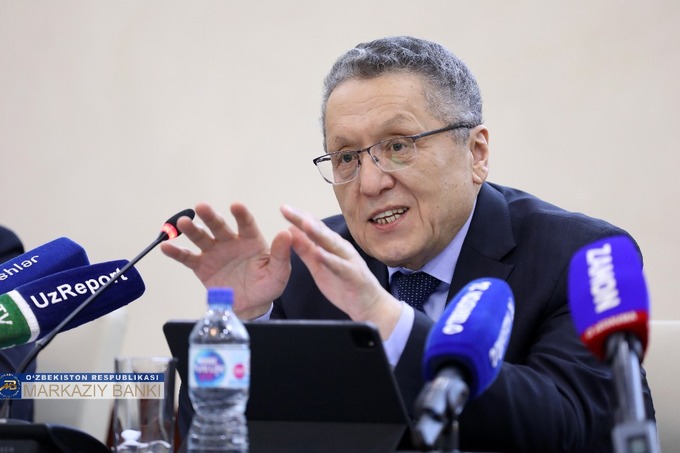
The Central Bank has postponed the achievement of a permanent inflation target of 5% to the end of 2024, although this target was originally planned to be achieved in 2023. This was stated at a press conference on July 21 by the chair of the Central Bank Mamarizo Nurmuratov.
In June, annual inflation stood at 12.2%, which is mainly due to imported inflation against the backdrop of global inflationary processes, disruptions in supplies and logistics, as well as the liberalization of grain selling prices, the head of the Central Bank said.
According to polls in June, inflation expectations of the population for the next 12 months show a downward trend, falling to 16.4% (against 17.6% in May). Inflationary expectations of entrepreneurs also fell to 15.7% (17.3% in May).
Weekly consumer price observations indicate that the weekly rate of price growth peaked in late May and early June and stabilized in the first two weeks of July.
In addition, in June, the prices for basic foodstuffs in the world according to the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) index began to form with a downward trend. Prices for oil, grain and sugar decreased by 7.6%, 4.1% and 2.6% respectively, while the monthly increase in prices for meat products amounted to 1.6%.
The Central Bank previously set the goal of achieving inflation below 10% in 2021 and 5% in 2023. At the end of last year, inflation fell to 9.98%, but geopolitical events, price trends for basic food products in the world, supply problems and interruptions in logistics show that high inflation risks and uncertainties will remain next year.
“This, in turn, creates the prerequisites for achieving the inflation target of 5% not in 2023, but in the second half of 2024. For this reason, taking into account the listed fundamental factors, the horizon for achieving the inflation target was decided to be postponed from 2023 to the end of 2024,” said Mamarizo Nurmuratov.
Since 2020, the Central Bank has begun to switch to inflation targeting. A permanent inflation target for 2023 was set at 5%. Earlier, the regulator explained the choice of the inflation target of 5% and the possible consequences if the rate is above and below 5%.